Applications for Refractory Oxides
Calculate the following based on your actual oxide chemistry:
Application Examples
Design of EBC-TBC Coatings
Advanced gas turbine blades rely on ceramic coatings to protect engine components in harsh combustion environments. These coatings are susceptible to accelerated degradation caused by silicate deposits formed when ingested environmental debris (dust, sand, ash) adheres to the coatings.
In this example, the yttrium silicate system was used as a case study to assess the utility of phase equilibrium modeling using the TCOX database in examining the factors controlling the interaction between coatings and silicate deposits. To replicate the progressive dissolution of the coating into the melt, the phase equilibria were calculated at 1300°C for incremental Y2Si2O7 additions to a fixed quantity of C33M9A13S45 deposit.
This calculation increases the size of the reacting system for successive Y2Si2O7 additions, just as the volume of material contained in the reaction layer increases with recession depth. By changing deposit compositions and reaction temperatures, researchers can understand how they will influence the depth of coating recession.
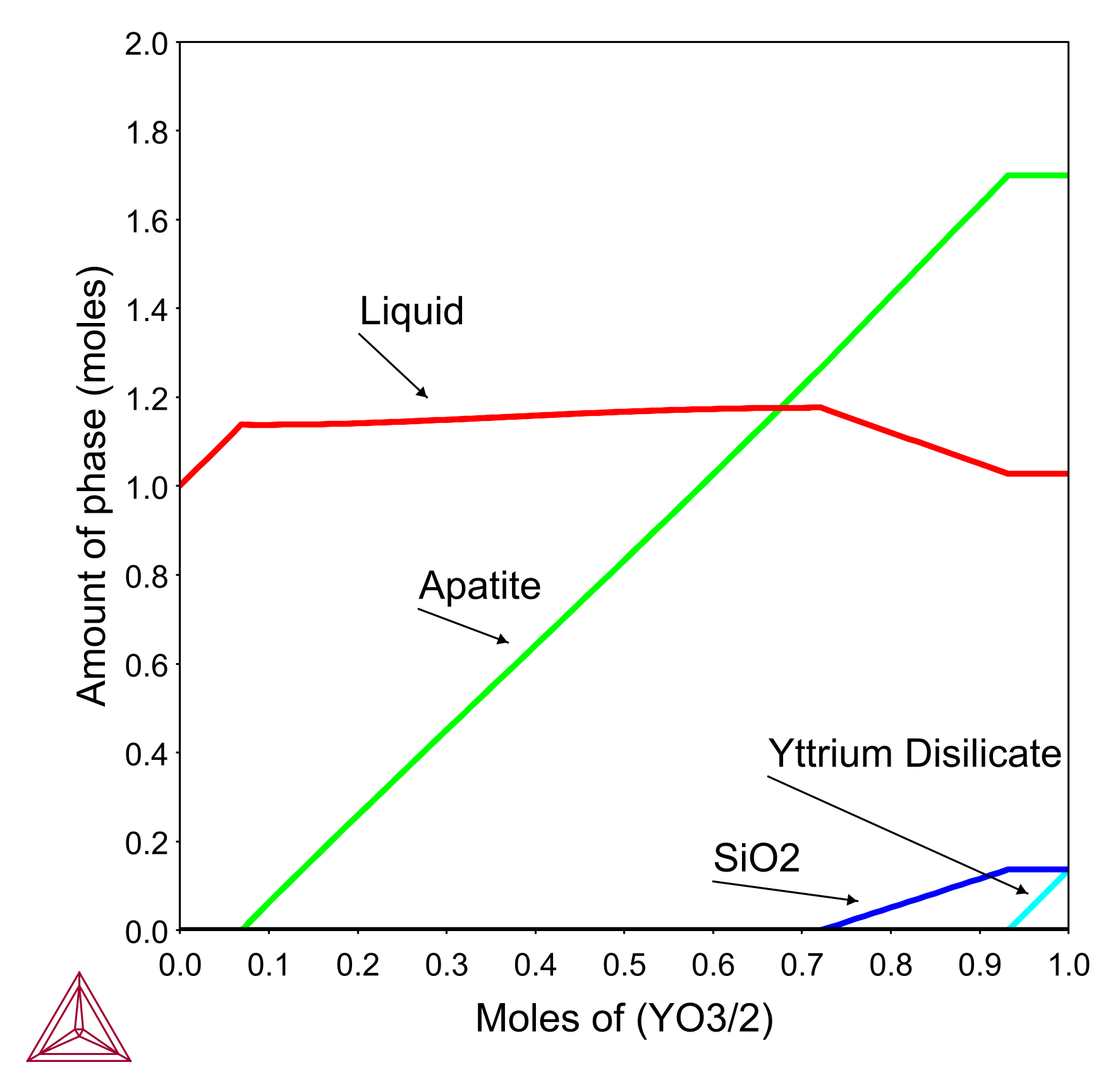
Phase equilibria calculation at 1300°C for incremental Y2Si2O7 additions to a fixed quantity of C33M9A13S45 deposit.
Products Related to Refractory Oxides
Learn more about Applications to Refractory Oxides
A video tutorial demonstrating how to calculate a phase diagram for the oxide system Al2O3-MgO.
Developments in Thermodynamic Models of Deposit-Induced Corrosion of High-Temperature Coatings
Improving Steel and Steelmaking—an Ionic Liquid Database for Alloy Process Design
Performance Comparisons between Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Compositions at various Temperatures and Proportions