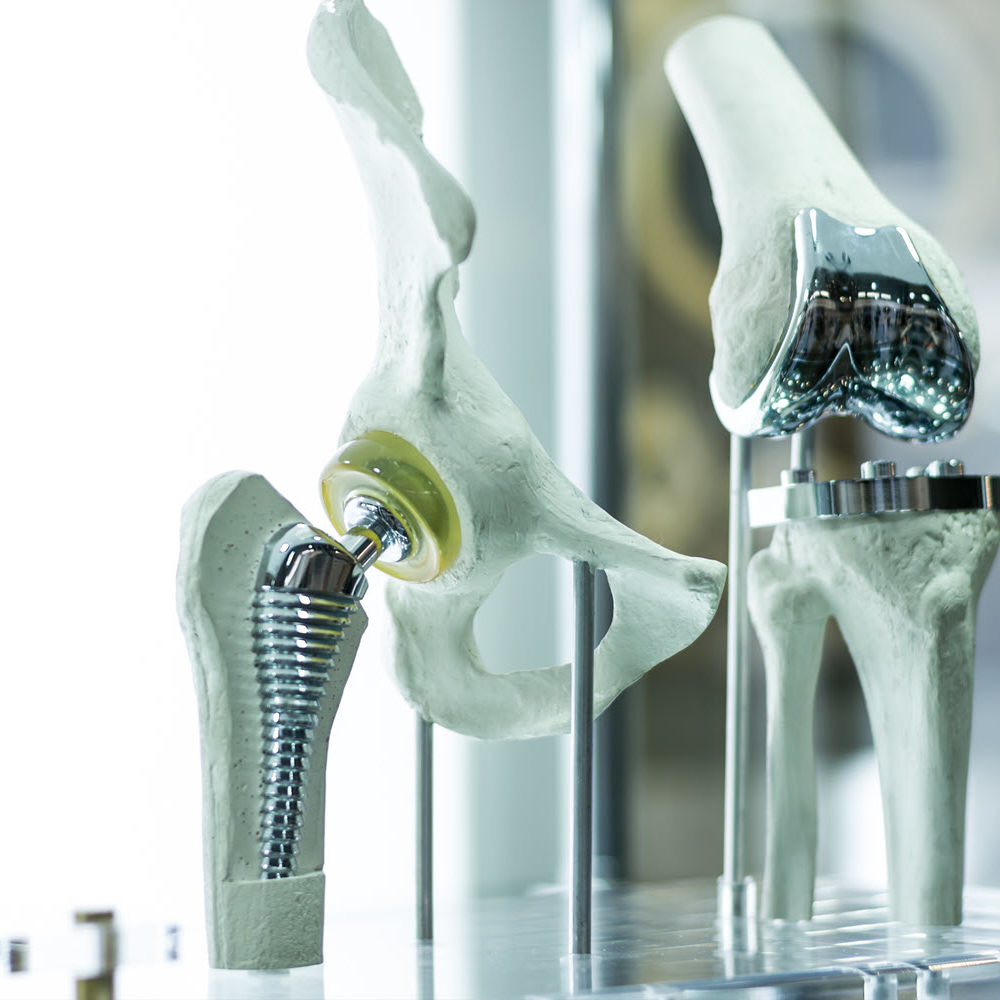
Applications for Titanium / TiAl Alloys
Calculate the following based on your actual alloy chemistry:
Application Examples
Calculate Beta Approach Curves
The β-transus temperature in titanium alloys plays an important role in the design of thermo-mechanical treatments. It primarily depends on the chemical composition of the alloy and is sensitive to the actual alloy chemistry. The oxygen content also has a big effect on the stability of the alpha phase. A beta approach curve shows the fraction of beta phase as a function of temperature and is useful when designing heat treatments to obtain specific properties.
This figure shows a beta approach curve for a Ti-6-2-4-2 alloy calculated in Thermo-Calc along with experimental data from Semiatin et al., Metall. Mater. Trans. A, vol. 38, no. 4, pp. 910–921, 2007.

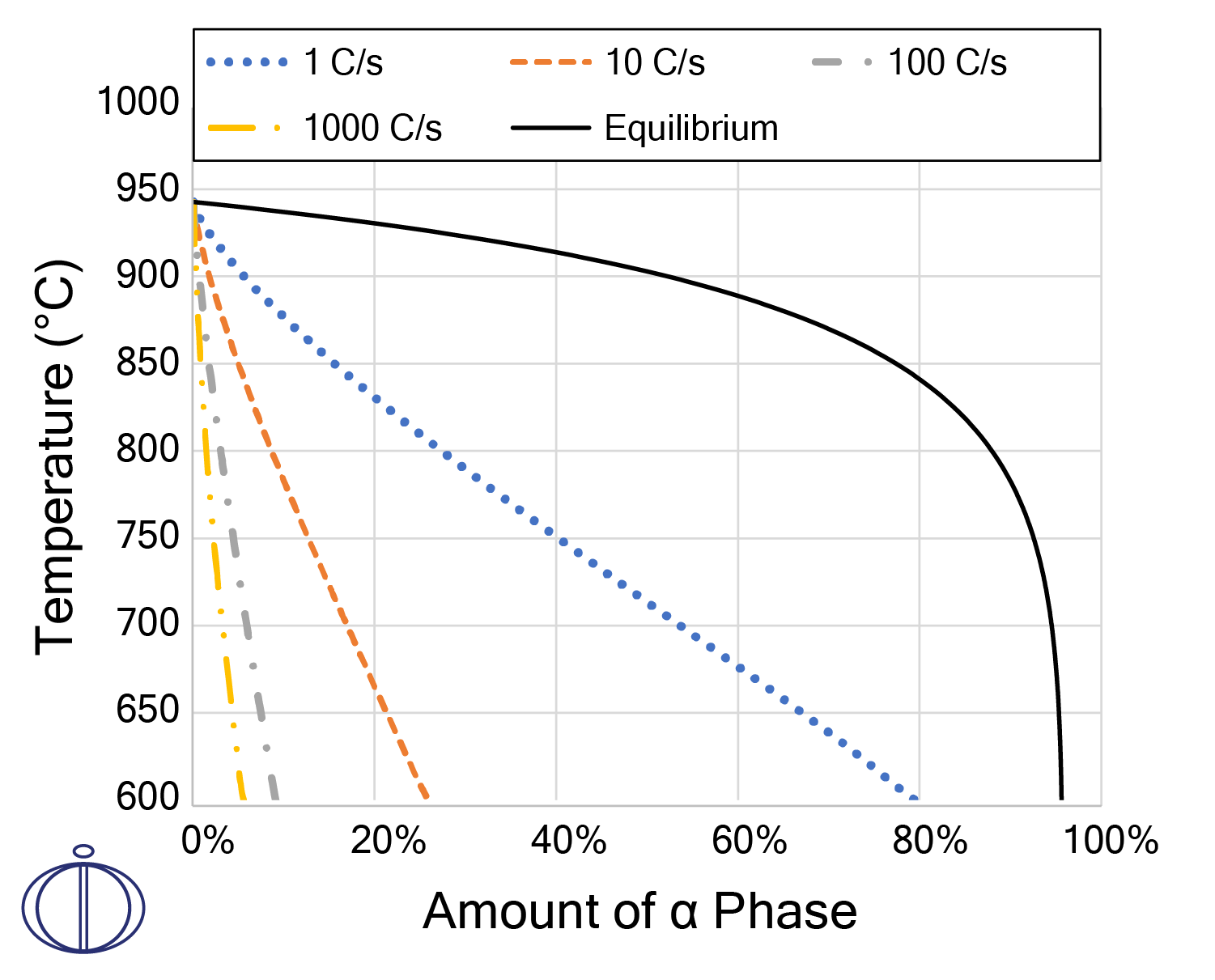
Predict Phase Balance as a Function of Cooling Rate
There is an inherent relationship between the material microstructure and the final material properties of a component. In titanium alloys, the balance of alpha/beta phases plays a major role in determining the final mechanical, corrosion, and creep properties. This phase balance can vary as a function of cooling rate. Thermo-Calc can simulate phase balance and precipitation behavior as a function of thermal history.
This figure shows the simulated amount of alpha phase in Ti-6Al-4V alloys as a function of cooling rate from 950 °C using the Diffusion Module (DICTRA) (recalculated based on data from Martukanitz et al., Addit. Manuf., vol. 1–4, pp. 52–63, 2014). The final amount of alpha is reduced as the cooling rate is increased.
Calculate Bulk and Young’s Modulus as a Function of Composition
Ti-alloys are a popular choice for biomedical implants due to their high yield strength, good ductility, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. However, the Young’s modulus mismatch between Ti- (>100 GPa) and human cortical bone (10-32 GPa) can lead to implant failure, thus making them difficult to use.
Thermo-Calc’s Titanium Databases have modelled elastic properties of Ti-alloys, which can be plotted as a function of composition and temperature, thus helping to predict Ti-alloy behavior conducive for biomedical applications. The example here is from Alberta et al., 2023, wherein the Young’s and Bulk modulus of a Ti-45Nb-xGa BCC β Ti-alloy is shown. Ga, one of the elements in the TCTI Database, is important because it is considered to lower the overall Young’s modulus and have potential bactericidal activity.

Products Related to Titanium and TiAl
Learn more about Applications to Ti/TiAl-based Alloys
Next Generation Database for Greener and More Efficient Aerospace Vehicles
Electron Beam Melting of a β‐Solidifying Intermetallic Titanium Aluminide Alloy
Design of High Temperature Ti–Al–Cr–V Alloys for Maximum Thermodynamic Stability Using Self-Organizing Maps