Applications to Corrosion
Calculate the following as a function of material chemistry and temperature:
Application Examples
Pourbaix Diagram Calculations for Pure Substances
Pourbaix diagrams are typically found in the literature for pure elements or only the most common alloys. As such, they often need to be determined experimentally, which can be costly and time consuming and still does not capture the composition variation that may be associated with an alloy. Using the Aqueous Calculator, included in Thermo-Calc, it is possible to make such predictions specifying both the alloy composition and also the solution chemistry.
In this example, the calculation for a 2.25Cr-1Mo steel readily maps the regions associated with immunity (H2 Gas Reducing Area), passivity (Fe2O3 and Fe3O4), as well as the region where corrosion readily occurs. The results correspond well with the data found in traditional handbooks.

Pourbaix Diagram Calculations for Alloys
The Aqueous Calculator in Thermo-Calc can also create Pourbaix diagrams for multicomponent alloys in aqueous solutions that contain other solutes (such as chlorides or sulfides). The example plots show the effect of alloy additions on the stability of the passive regions relative to the pure Fe example shown previously. The left plot is the Cr-Mo steel and the right plot is a 304SS (18Cr-8Ni) alloy. Additional Cr content can further stabilize this passive region in chloride containing environments, such as seawater. The calculator can be used to calculate thermodynamic stability from ambient temperature and pressure up to 350°C and 100 bar. To see the plot larger, right click and select “Open image in new tab.”
See a poster with several examples of Thermo-Calc’s applications to corrosion aqueous solutions.

High Temperature Oxidation in Supercritical Water Reactor Service
Some high efficiency nuclear reactors rely on operating at conditions above the thermodynamic critical point of water, termed supercritical water reactors. Supercritical water is more corrosive than traditional reactor water solutions, which places challenges on design by requiring materials that maintain strength at high temperatures and are resistant to both corrosion and irradiation. This figure shows a calculation of oxide formation and stability as a function of the partial pressure of oxygen. This calculation reveals that 12Cr steels can form a complex layered oxide under normal reactor operating conditions.
See a poster with several examples of Thermo-Calc’s applications to corrosion at high temperatures.

Design of EBC-TBC Coatings
Advanced gas turbine blades rely on ceramic coatings to protect engine components in harsh combustion environments. These coatings are susceptible to accelerated degradation caused by silicate deposits formed when ingested environmental debris (dust, sand, ash) adheres to the coatings.
In this example, the yttrium silicate system was used as a case study to assess the utility of phase equilibrium modeling using the TCOX database in examining the factors controlling the interaction between coatings and silicate deposits. To replicate the progressive dissolution of the coating into the melt, the phase equilibria were calculated at 1300°C for incremental Y2Si2O7 additions to a fixed quantity of C33M9A13S45 deposit.
This calculation increases the size of the reacting system for successive Y2Si2O7 additions, just as the volume of material contained in the reaction layer increases with recession depth. By changing deposit compositions and reaction temperatures, researchers can understand how they will influence the depth of coating recession.
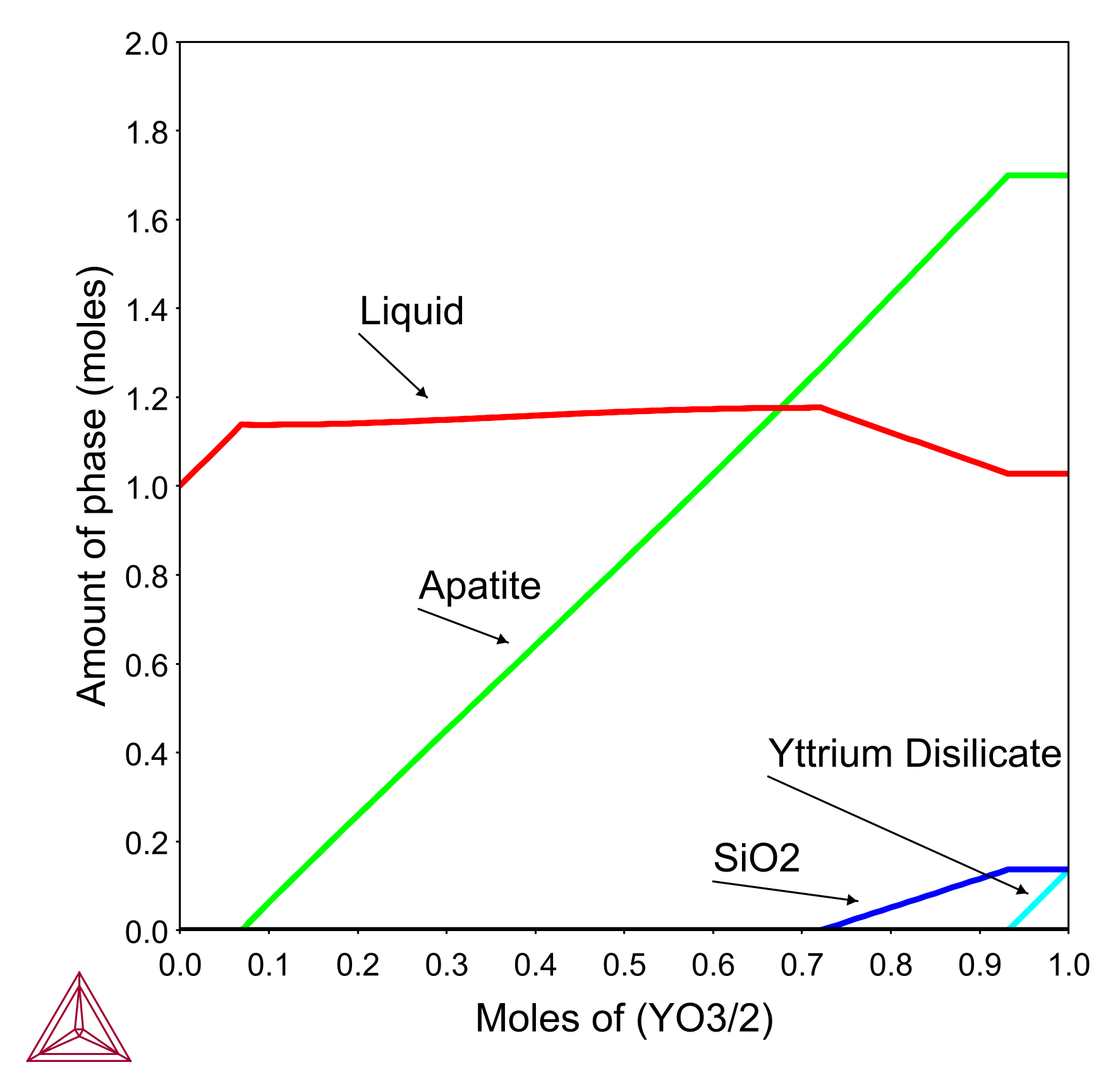
Phase equilibria calculation at 1300°C for incremental Y2Si2O7 additions to a fixed quantity of C33M9A13S45 deposit.
Learn more about Applications to Corrosion
Potential-pH diagrams considering complex oxide solution phases for understanding aqueous corrosion of multi-principal element alloys
Learn how Thermo-Calc can be used to make a Pourbaix diagram for a 304 Stainless Steel in this free lesson from our Learning Hub
Integrated computational materials engineering of corrosion resistant alloys
Solving Corrosion Challenges with Integrated Computational Materials Modeling
Corrosion of Multicomponent Multiphase Materials in Aqueous Solutions under Various Temperature, Pressure and Molality
High Temperature Corrosion of Multiphase, Multi- component Alloys in Gaseous Atmospheres under Varying partial pressure of Oxygen, Sulphur and Carbon
Materials Corrosion Applications with Thermo-Calc
A module within Thermo-Calc that allows you to predict materials corrosion resistance.
High corrosion resistance duplex fcc + hcp cobalt based entropic alloys: An experimental and theoretical investigation